Welcome to Izine
Your source for Generalist (EN) insights. Explore our articles and guides.

Our topics
Explore all our Generalist (EN) content
Automotive
Cars, vehicles and driving
Business
Business and economy
Cooking
Recipes and culinary arts
Finance & real estate
Finance, investment and property
Health
Health, wellness and wellbeing
Home & living
Home, decor and lifestyle
News
Latest news and current events
Pets
Pets, animals and companions
Sports
Sports, fitness and competition
Technology
Tech, gadgets and innovation
Woman / fashion
Fashion, beauty and lifestyle
Latest articles
Our recent publications

How are UK car manufacturers adapting to emission regulations?
The UK car manufacturers are accelerating their investment in electric vehicles (EVs) to comply with tightening emission...

What role does government policy play in the UK automotive sector?
Government regulation automotive industry plays a crucial role in shaping the UK automotive policy landscape. The UK car...

What strategies are UK automotive companies using to attract talent?
The UK automotive sector faces significant talent attraction challenges, including a competitive job market and a demand...

How can UK businesses foster a culture of innovation?
Building an innovation culture in UK businesses begins with embedding innovation in company values and mission. When inn...

What are the best practices for UK businesses to enhance customer loyalty?
When focusing on customer loyalty strategies UK, one of the most effective approaches involves implementing well-structu...

What are the key factors driving innovation in UK industries?
Innovation drivers UK revolve significantly around government policy and funding. The UK government plays a crucial role...

How can you make a traditional spotted dick from scratch?
Creating an authentic spotted dick requires a precise combination of ingredients and the right tools to achieve the clas...

How do you bake a light and fluffy spotted dick?
Choosing the right spotted dick ingredients is crucial for creating an authentic traditional British dessert. The classi...

What are the essential steps for making a homemade Lancashire hotpot?
Lancashire hotpot is a traditional British dish deeply rooted in the culinary history of North West England. Its origins...

How Can Savvy Investment in UK Real Estate Drive Economic Growth?
Strategic UK real estate investment plays a significant role in driving economic growth by stimulating various sectors o...

How is the Housing Market in the UK Shaped by Global Economic Trends?
Global economic conditions exert a strong influence over the UK property market, shaping demand, pricing, and investor b...

What role do REITs play in the UK property investment landscape?
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) are influential financial instruments within the UK property investment landscape....

How Is Mental Health Awareness Evolving in the UK?
The landscape of mental health awareness UK has undergone significant changes in recent years, marked by notable shifts ...

How is the UK improving healthcare access for marginalized communities?
The UK healthcare policy landscape has seen significant government action to address health disparities affecting margin...

What innovative technologies are transforming UK healthcare?
The UK healthcare technology innovations landscape is evolving rapidly, introducing transformative health tech that addr...

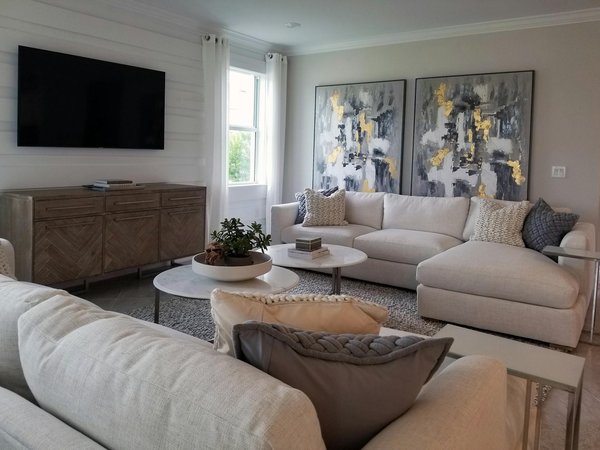
How can you design a cozy reading nook in your UK home?
Creating a cozy reading nook UK starts with smartly assessing your available space. Look for natural alcoves, bay window...

How can you integrate biophilic design into your UK living space?
Biophilic design UK focuses on reconnecting UK homes with nature through core principles that enhance wellbeing and comf...

How Can You Update Your UK Home on a Budget?
When planning budget home improvement UK, focusing on high-impact, low-cost projects is key. Small changes like repainti...

How can you train your pet for UK apartment living?
Training pets in UK apartments requires a carefully tailored approach that accounts for limited space and close neighbou...

How can you travel with your pet within the UK?
Exploring how to move your pet safely and comfortably...
What are the best pet-friendly accommodations in the UK?
Discovering the best UK hotels for pets involves finding places where both pets and owners feel truly welcomed. Many pet...

How does Brexit affect UK sports partnerships?
The legal impact of Brexit on UK sports has been profound, with the UK needing to develop new legal frameworks to replac...

What are the key challenges facing women's sports in the UK?
Women's sports in the UK face persistent challenges that hinder growth and equality. Central to these issues is gender i...

What impact does Brexit have on UK sports talent recruitment?
Since Brexit, UK sports recruitment has undergone significant transformation due to the new regulatory landscape. The Br...

How are UK tech companies promoting diversity and inclusion?
UK tech sector leaders prioritize diversity and inclusion strategies that foster genuine workplace inclusion. A primary ...

What role does AI play in shaping the future of UK technology?
The United Kingdom is at the forefront of a technological revolution, and artificial intelligence (AI) is a key driver o...

What role does UK technology play in smart city development?
Smart city development in the UK relies heavily on cutting-edge technology advancements that merge urban innovation with...

How Can You Incorporate Retro Styles Into Your Wardrobe?
...
Join our community
Stay informed about Generalist (EN).
Rejoindre →